Introduction
In the world of electronics, one of the first and most important concepts you’ll encounter is understanding the difference between series and parallel circuits. Whether you’re a school student, an engineering beginner, or a DIY electronics lover, this knowledge helps you build, troubleshoot, and improve your electrical projects.
This detailed guide explains:
What series and parallel circuits are
Key differences between them
How they work in real-life situations
Easy formulas, examples, and diagrams
Safety, efficiency, and applications
Let’s simplify electronics together!
What is an Electrical Circuit?
An electrical circuit is a closed path where electric current flows from a power source through components like bulbs, motors, or resistors and returns to the source.
There are two main types:
Series Circuit
Parallel Circuit
Understanding how these circuits work is crucial for designing efficient and safe electrical systems.
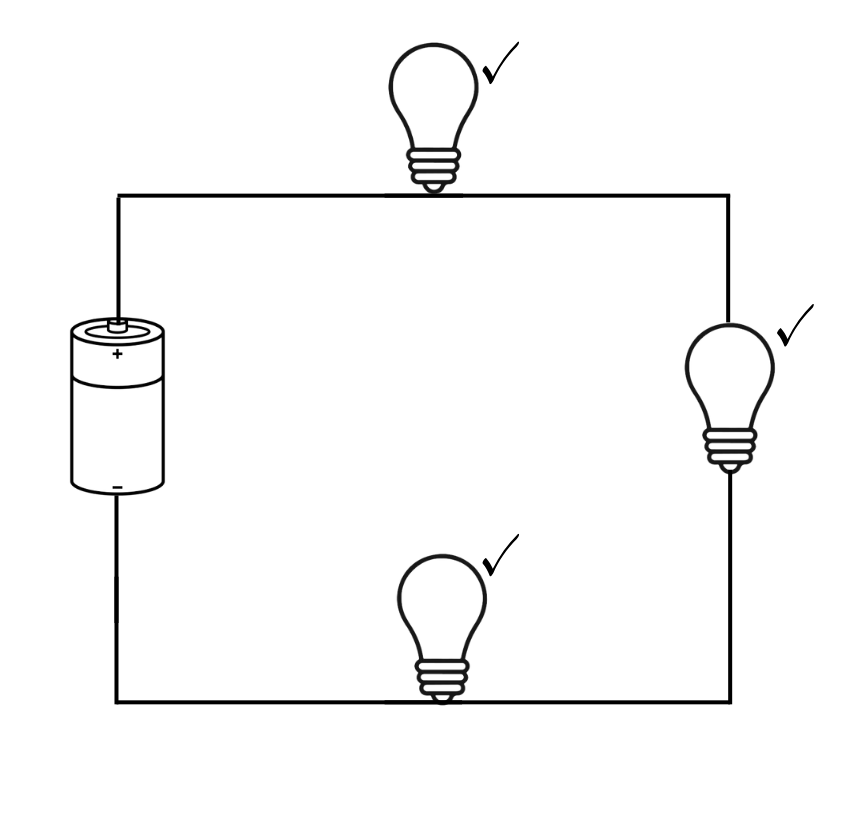
Series Circuit:
A series circuit connects all components one after another—like a chain. The same current flows through every component.
Features of a Series Circuit:
One single path for current
Current remains the same across all components
Voltage is shared among components
Total resistance = sum of all resistors
If one component fails, the entire circuit breaks
Formula:
R<sub>total</sub> = R₁ + R₂ + R₃ + …
Example:
Old Christmas lights: One bulb goes out, the whole string turns off.
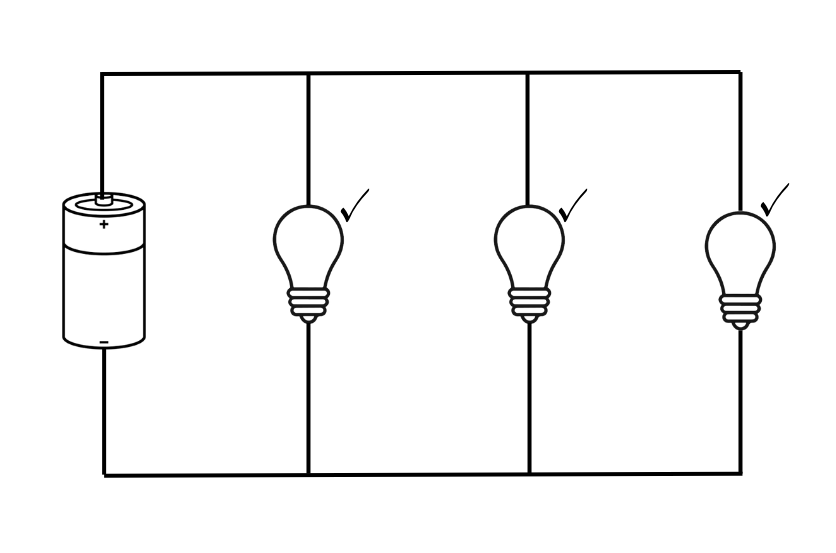
Parallel Circuit:
A parallel circuit connects each component on its own separate branch across the same power source. This allows current to split and flow through different branches.
Features of a Parallel Circuit:
Multiple paths for current
Same voltage across each component
Current divides among branches
Total resistance is less than the smallest resistor
If one component fails, others keep working
Formula
1/R<sub>total</sub> = 1/R₁ + 1/R₂ + 1/R₃ + …
Example
Home wiring: If one light bulb fails, others still stay on.
Series vs Parallel Circuit: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| Current | Same in all components | Splits across branches |
| Voltage | Divided across components | Same for all branches |
| Resistance | Adds up | Decreases |
| Effect of One Failure | Entire circuit stops working | Only that branch stops |
| Energy Efficiency | Less efficient for multiple devices | More efficient for distribution |
| Wiring Complexity | Simple | More complex |
| Example | Flashlight, old fairy lights | Home wiring, power strips |
Real-Life Applications
Where Series Circuits Are Used:
Flashlights – Simple layout, low-power devices
Electric kettles – Heat elements in line
Old Christmas lights
Burglar alarm systems – Sequential triggering
Where Parallel Circuits Are Used:
Home electricity systems – For lights and sockets
Cars and bikes – Electrical systems
Refrigerators and TVs – Individual functioning
LED lighting systems – Independent operation
Performance and Power Efficiency
Series Circuit:
Power shared among components
Less efficient when more devices are added
Voltage divides, which can weaken device output
Parallel Circuit:
Devices get full voltage
Higher overall current
Better power delivery for modern applications
Safety Considerations
Series circuits are suitable for simple, low-power devices.
Parallel circuits are used in homes and industries for reliable and safe operation.
Parallel allows fault isolation—one device fails, the rest stay active.
Advanced Use Cases
| Application Area | Series Circuit Use | Parallel Circuit Use |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Packs | Series for higher voltage | Parallel for longer usage (more Ah) |
| Solar Panels | Series increases voltage | Parallel increases current |
| Sensors and Controls | Used in chains | Used for redundancy and safety |
| Capacitor Banks | Rarely in series | Commonly in parallel |
Troubleshooting Tips
Series Circuit Problems:
One device not working = whole circuit fails
Use a multimeter to check continuity step-by-step
Parallel Circuit Problems:
Single failure easy to isolate
Check branch-wise to find faulty part
Quick Quiz: Test Your Circuit Knowledge
What happens to current in a series circuit when you add a resistor?
What’s the voltage across branches in a parallel circuit with a 9V battery?
Which circuit type is better for independent device operation?
Drop your answers in the comments — let’s see who gets them all right!
About pluntx

Pluntx is India’s leading platform for electronics and 3D printing solutions, offering a wide range of products like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, drone parts, sensors, 3D printer components, and more. We also provide expert CAD design services and affordable 3D printing, starting at just ₹49. Click here to explore our extensive collection of electronics and prototyping tools. Be sure to follow us on Instagram and YouTube, where we regularly share tutorials, tips, and updates on everything from Arduino projects to drone technology. Pluntx delivers precision and quality. Our mission is to empower creativity through technology and simplify the journey from concept to creation.
